2020
Baumann, D., Solowjow, F., Johansson, K. H., Trimpe, S.
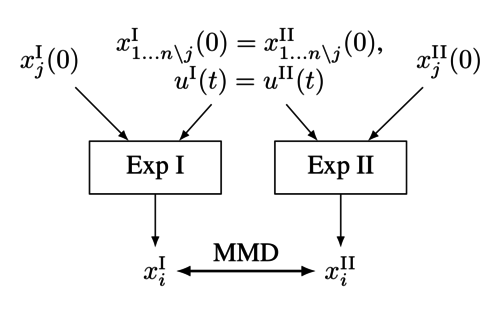
Identifying Causal Structure in Dynamical Systems
2020 (techreport)
2019
Mager, F., Baumann, D., Jacob, R., Thiele, L., Trimpe, S., Zimmerling, M.
Demo Abstract: Fast Feedback Control and Coordination with Mode Changes for Wireless Cyber-Physical Systems
Proceedings of the 18th ACM/IEEE Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), pages: 340-341, 18th ACM/IEEE Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), April 2019 (poster)
2018
Mager, F., Baumann, D., Trimpe, S., Zimmerling, M.
Poster Abstract: Toward Fast Closed-loop Control over Multi-hop Low-power Wireless Networks
Proceedings of the 17th ACM/IEEE Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), pages: 158-159, Porto, Portugal, April 2018 (poster)
2016
Ebner, S., Trimpe, S.
Supplemental material for ’Communication Rate Analysis for Event-based State Estimation’
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, January 2016 (techreport)
2015
Trimpe, S.
Distributed Event-based State Estimation
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, November 2015 (techreport)